Differences Between Perforated Metal Sheets and Plain Metal Sheets
Source:www.cn-psp.cnAuthor:河北森驰公司 Last updated:2025-03-04 13:16:31 Browse:
In industrial and architectural fields, metal sheets are widely used in various scenarios. However, not all metal sheets are the same. Significant differences exist between perforated metal sheets and plain metal sheets, impacting not only their appearance but also their functionality and application scope.
Design and Appearance
Perforated Metal Sheets
Perforated metal sheets undergo specialized processing to feature regular or irregular holes on their surface. These holes can be customized in shape (e.g., round, square, triangular) and adjusted in size and spacing according to client requirements. This unique design offers an aesthetic and creative appearance, making them ideal for decorative purposes.
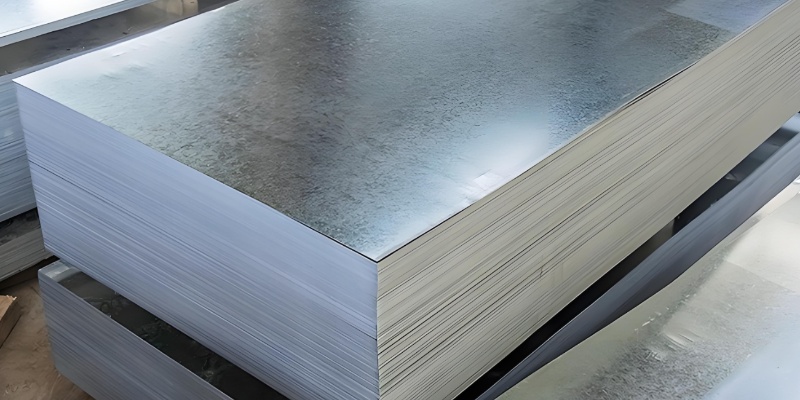
Plain Metal Sheets
In contrast, plain metal sheets typically retain their original flat form without additional surface treatments. While their appearance can be enhanced through painting or polishing, they lack the distinctive visual appeal of perforated sheets.
Functional Properties
Acoustic Performance
Perforated metal sheets excel in acoustics due to their porous structure. The holes allow partial sound penetration, enabling noise absorption and reduction. This makes them suitable for venues like concert halls and conference rooms requiring precise sound control.
Ventilation and Heat Dissipation
The perforations enhance airflow, making these sheets ideal for applications requiring ventilation or heat dissipation, such as HVAC system covers or equipment cooling panels.
Weight Reduction
By removing material to create holes, perforated sheets are lighter than plain sheets of the same size. This advantage simplifies transportation and installation, particularly in high-rise buildings or large-scale projects.

Application Scenarios
Perforated Metal Sheets
Architectural Decoration: Curtain walls, ceilings, partition walls.
Filtration and Separation: Screening equipment in chemical, food processing, and pharmaceutical industries.
Protection and Shielding: Safety guards for machinery, electromagnetic shielding covers.
Plain Metal Sheets
Structural Support: Foundational components in construction or machinery.
Surface Cladding: Protective layers or substrates for other materials.
Conclusion
In summary, the key distinction lies in the perforation process: perforated sheets offer unique aesthetics and enhanced functionality (acoustic control, ventilation, weight reduction), while plain sheets prioritize durability and structural integrity. Selecting the right material depends on project-specific needs to achieve optimal results.

